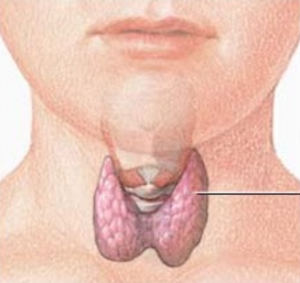
A 2017 summary of the research literature supports the idea that optimal selenium levels are needed for antioxidant protection against harmful free radicals in the thyroid gland and for the normal metabolism of thyroid hormones [Ventura 2017].
A 2018 research literature review shows that selenium supplementation can reduce anti-thyroperoxidase antibody levels and can improve thyroid ultrasound features. In addition, selenium supplementation is associated with improved symptoms and improved quality of life in patients with Graves orbitopathy [Santos 2018].
Note: Anti-thyroperoxidase antibody levels that are too high (>500 IU/ml) are associated with an increased risk of hypothyroidism in autoimmune thyroiditis, which is the most common form of thyroid disorder [Ehlers 2016].