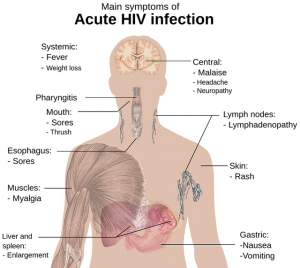
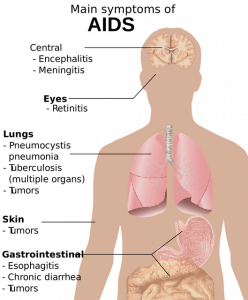
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is still very much a public health concern. Deficiencies of certain micronutrients are known to play a role in the progression of HIV infections to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). In particular, adequate intakes of selenium are important because of selenium’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in HIV infection [Pourmoradian 2023].
Umbrella Study of Systematic Reviews of Selenium and HIV Studies
In a 2023 umbrella study of systematic reviews of studies of selenium in HIV patients, Pourmoradian et al found the following evidence:
- Four reviews showed that selenium supplementation at the level of 200 mcg/day was effective in delaying CD4 decline in HIV-infected patients.
- Three reviews showed that selenium supplementation at the level of 200 mcg/day significantly reduced HIV viral load.
- The researchers suggested that the underlying mechanism of the selenium effect on HIV progression is the improvement of the immune response and the antioxidant defense system.
- In particular, the selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) enzyme system reduces the extent of oxidative stress, indirectly strengthens the immune system, and slows the progression of the disease.
Note: CD4 cells are lymphocytes that help to coordinate the immune response to infections. If an HIV patient’s CD4 cell count falls below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood, then the HIV infection is considered to have progressed to the AIDS stage. In healthy individuals, the CD4 count will be between 500 and 1,600 cells/cubic millimeter of blood.