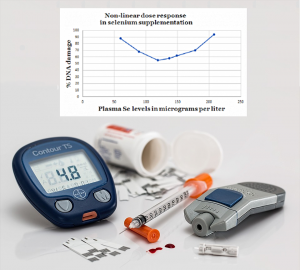
Researchers at the University of Arizona in Tucson, home of the Arizona Cancer Center, identified a statistically significant direct relationship between selenium and Type-2 diabetes in observational studies but no statistically significant relationship in randomized controlled trials [Kohler 2018].
Note: Randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for scientific evidence in the bio-medical field. The randomization of the study participants should produce comparable groups and should eliminate accidental bias. In observational studies, the researchers do not randomly assign the study participants to groups and do not decide which treatments each group receives or does not receive.

