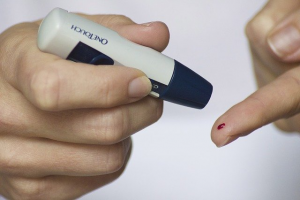
The effect of selenium supplementation on blood sugar levels and on the risk of diabetes is still an open question. However, the data from randomized controlled studies show that selenium supplementation is associated with either a beneficial effect or no effect at all on blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and glucose tolerance [Jablonska 2016].
Study Participants with Type-2 Diabetes
Beneficial effect. In a 2019 study, the participants were 72 male and 22 female patients aged 48 to 64 years old with diabetes mellitus type 2. They were smokers, all of them, and they all followed a Mediterranean diet.
The researchers administered selenium 200 microg/day once daily on an empty stomach. The study data showed a statistically significant reduction in the blood levels of glucose and in HbA1c values at both three months and six months after the beginning of the treatment. The administration of selenium to type-2 diabetic patients seemed to improve the patients’ glycemic profile [Karalis 2019].

