Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disease. It is a disease that causes underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). The body’s own immune-system cells attack the cells of the thyroid gland and gradually break them down and destroy them. This, of course, has a detrimental effect on thyroid gland function and on important metabolic processes in the body.
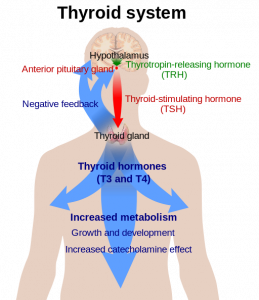
Hashimoto’s is a bit tricky. In its early development and progression, there may not be any obvious symptoms. Eventually, such symptoms as fatigue and lethargy and weight gain will make themselves manifest. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a debilitating disease. It lessens a person’s quality of life. It tends to affect women more than men.
Of all the organs in the body, the thyroid gland has the highest concentration of selenium. It is a greedy organ with respect to selenium. An adequate intake of selenium can lessen the severity of hypothyroidism symptoms and is associated with lowered levels of autoimmune thyroid peroxidase antibodies.