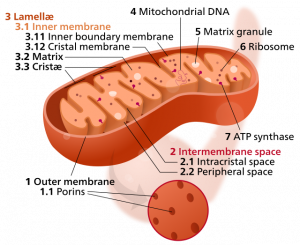
In individuals older than 50-60 years, the kidneys’ glomerular filtration rate decreases with increasing age. The glomerular filtration rate is a measure of how well your kidneys are working. In your kidneys, there are tiny filters (called glomeruli) that remove waste and excess fluid from the blood.

Exposure to toxic metals – mercury, cadmium, lead – can be detrimental to kidneys of normal adults. Accordingly, exposure to toxic metals can affect individuals with reduced glomerular filtration rates even more adversely.
Professor Jan Aaseth and a team of researchers have reviewed the available research data. Their findings show the following relationships [Aaseth 2021]:
- an association between exposure to the toxic metals and an increase in the incidence and severity of renal disease in elderly individuals
- an association between sufficient selenium status and protection against the degradation of kidney function caused by the metal pollutants
Elderly Individuals More Susceptible to Toxic Metal Exposure
Healthy elderly individuals are capable, for the most part, of maintaining normal kidney function. However, especially after the age of 70 years, physiological changes occur in the kidneys.