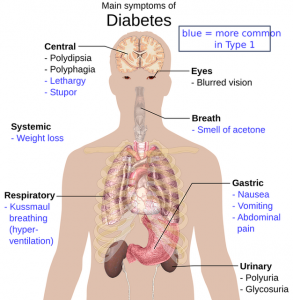
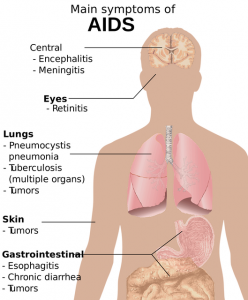
The rationale for taking a selenium-enriched yeast preparation: one or more of the selenium compounds in the preparation other than selenomethionine may be the selenium species that has specific effects against cancer. This is an area for further research.

This week, we focus on studies conducted with a selenium-enriched yeast preparation containing at least 20 different species of selenium in addition to selenomethionine [Bendahl & Gammelgaard 2004].
Randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trials are the gold standard method for testing the safety, absorption, and efficacy of nutritional supplements and medical drugs. Below, we summarize some of the important clinical trials of nutritional interventions using selenium-enriched yeast.