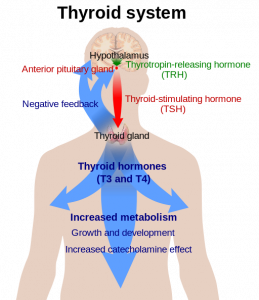
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disease. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, i.e., overactive thyroid disorder. Ultimately, it is the overproduction of thyrotropin receptor (TRAb) antibodies that results in hyperthyroidism. Over time, Graves’ disease causes extensive damage to thyroid gland cells and tissues [Song 2023].
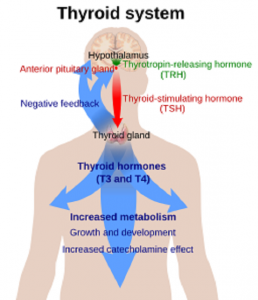
Oxidative stress appears to play an important role in Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Oxidative stress is the medical term for a disruption of the balance between harmful free radical oxidants and protective antioxidants. The increased production of reactive oxygen
radicals and inflammatory cytokines drives the development and progression of Graves’ disease [Song 2023].