In cases of severe Covid-19 disease, patients have significantly lower concentrations of selenium and selenoprotein P and significantly higher levels of oxidative stress. That is to say, there is a more intense formation of harmful free radicals in patients with severe Covid-19 disease [Skesters 2022].

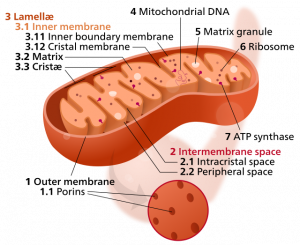
Note: Oxidative stress is the bio-medical term for an imbalance between harmful free radical activity and protective antioxidant activity. Selenium is a key component of antioxidant selenoproteins such as the glutathione peroxidases and the thioredoxin reductases.
Role of Selenium and Selenoprotein P in Covid-19 Disease
Researchers have been investigating the role that selenium may play in reducing the severity and mortality of Covid-19 infections. Studies have shown a close relationship between low selenium status, Selenoprotein P deficiency, oxidative stress level, and Covid-19 disease incidence, severity, and prognosis [Skesters 2022].